Improving the Segmentation and Visualization of Intracranial Aneurysms in 3D Angiograms
When segmenting and visualizing intracranial aneurysms in three-dimensional (3D) angiograms, there is often a tendency to overemphasize the neck of the aneurysm, whereas its nature plays a crucial role in the morphological analysis for selecting the appropriate interventional procedure. Using two-dimensional (2D) angiographic imaging, the true morphology can be more accurately assessed if the projection direction is appropriate. On the one hand, such 2D data are obtained in the form of additional high-resolution images during diagnosis or intervention. On the other hand, they are available in the form of lower resolution 2D raw data from the acquisition of the 3D images themselves.
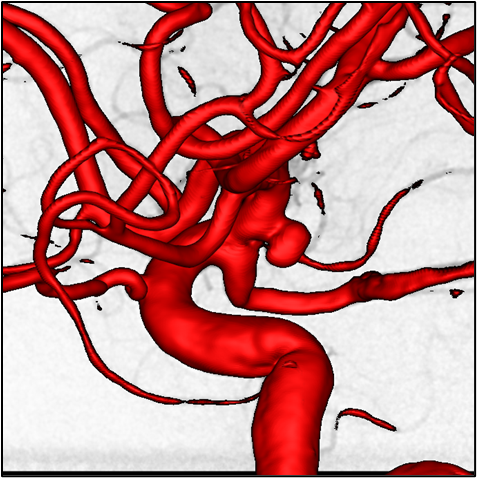
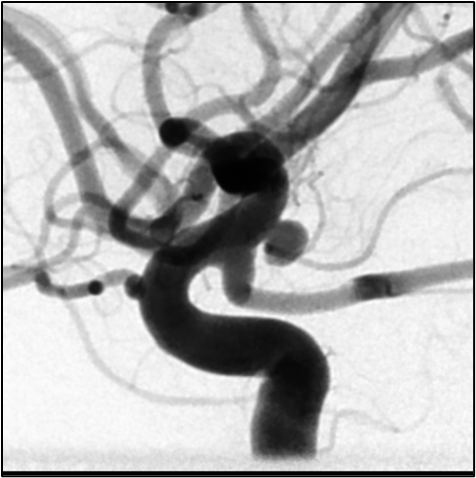
In this thesis, both types of 2D images will be tested for their suitability to be used as an automated mask for the optimization of 3D visualization and segmentation in order to improve the morphological quality of 3D visualization and segmentation.
The implementation will be done in Python using the open source tools Visualization Toolkit (VTK – https://vtk.org) for segmentation and visualization and if necessary Insight Toolkit (ITK – https://itk.org) or SimpleITK (https://simpleitk.org) for any necessary registration between 2D and 3D image series.
Type: Bachelor/ or Master Thesis
Requirements: Good skills in scientific reading; critical thinking; good skills in programming (Python, VTK and related toolkits)



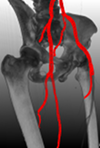 Erkrankungen des Blutkreislaufs gehören zu den am weitesten verbreiteten Krankheiten in Industrienationen. So starben alleine in Deutschland im Jahr 2001 insgesamt 290.000 Personen an Erkrankungen des Herz-Kreislauf-Systems. Zuverlässige Diagnosesysteme und eine Verbesserung bestehender Verfahren sind daher von großer Bedeutung. Eine zentrale Aufgabe stellt hierbei eine geeignete Visualisierung des segmentierten Blutflußbaums beziehungsweise einzelner, erkrankter Abschnitte der Blutgefäße dar.
Erkrankungen des Blutkreislaufs gehören zu den am weitesten verbreiteten Krankheiten in Industrienationen. So starben alleine in Deutschland im Jahr 2001 insgesamt 290.000 Personen an Erkrankungen des Herz-Kreislauf-Systems. Zuverlässige Diagnosesysteme und eine Verbesserung bestehender Verfahren sind daher von großer Bedeutung. Eine zentrale Aufgabe stellt hierbei eine geeignete Visualisierung des segmentierten Blutflußbaums beziehungsweise einzelner, erkrankter Abschnitte der Blutgefäße dar.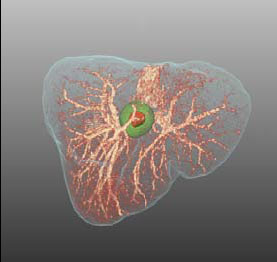 Chirurgische Eingriffe an der Leber, etwa zur Entfernung von Tumoren, gelten aufgrund der komplexen Struktur der Blutversorgung innerhalb der Leber als besonders schwierig. Für eine erfolgreiche Operation ist die genaue Kenntnis des Verlaufs der Blutgefäße von entscheidender Bedeutung, da sich an ihnen die Schnittführung der Resektion orientiert.
Chirurgische Eingriffe an der Leber, etwa zur Entfernung von Tumoren, gelten aufgrund der komplexen Struktur der Blutversorgung innerhalb der Leber als besonders schwierig. Für eine erfolgreiche Operation ist die genaue Kenntnis des Verlaufs der Blutgefäße von entscheidender Bedeutung, da sich an ihnen die Schnittführung der Resektion orientiert.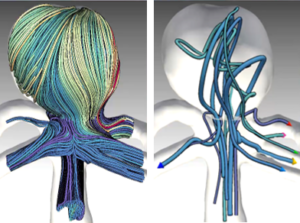 In cerebral aneurysm research, CFD simulations allow us to gain a better understanding of the dynamics of the blood flow. The simulated flow is often visualized using integral curves resulting in cluttered “spaghetti plots”. Advanced approaches group similar curves and show only selected representatives (image). These approaches however, fail in showing the clusters’ spatial extent. In this thesis, an interactive approach facilitating a continuous transition between the full set of integral curves and an uncluttered abstracted visualization shall be developed. Browsing back and forth through various levels of abstraction shall allow the user to grasp both, the general structure of the blood flow pattern as well as the spatial extent of individual substructures.
In cerebral aneurysm research, CFD simulations allow us to gain a better understanding of the dynamics of the blood flow. The simulated flow is often visualized using integral curves resulting in cluttered “spaghetti plots”. Advanced approaches group similar curves and show only selected representatives (image). These approaches however, fail in showing the clusters’ spatial extent. In this thesis, an interactive approach facilitating a continuous transition between the full set of integral curves and an uncluttered abstracted visualization shall be developed. Browsing back and forth through various levels of abstraction shall allow the user to grasp both, the general structure of the blood flow pattern as well as the spatial extent of individual substructures.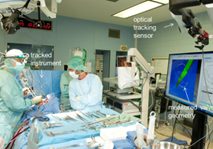 Im Rahmen der Arbeit sollen Stereoverfahren für die 3D-Rekonstruktion von Strukturen aus intraoperativen Endoskopiebildern entwickelt werden. Die Arbeit wird in enger Kooperation zwischen der Fakultät Informatik der OvGU Magdeburg (Dr. Sandy Engelhardt) und der Herzchirurgie des Universitätsklinikums Heidelberg (Prof. De Simone) durchgeführt. Weitere Themen für Abschlussarbeiten sind vorhanden. Melden Sie sich gern bei Interesse.
Im Rahmen der Arbeit sollen Stereoverfahren für die 3D-Rekonstruktion von Strukturen aus intraoperativen Endoskopiebildern entwickelt werden. Die Arbeit wird in enger Kooperation zwischen der Fakultät Informatik der OvGU Magdeburg (Dr. Sandy Engelhardt) und der Herzchirurgie des Universitätsklinikums Heidelberg (Prof. De Simone) durchgeführt. Weitere Themen für Abschlussarbeiten sind vorhanden. Melden Sie sich gern bei Interesse.